From 1 piece to mass production, our one-stop custom services ensure a worry-free experience for you.
Help Center
Views: 222 Author: Loretta Publish Time: 2025-12-26 Origin: Site
Content Menu
● Core Keywords and Buyer Intent
● High Efficiency In Mass Production
● Precision And Complex Geometry
● Rapid Production Cycles And Time To Market
● Wide Range Of Materials And Applications
● Cost Effectiveness For Large Production Runs
● Design Flexibility And Functional Integration
● Minimal Post Processing And High Surface Quality
● Sustainability And Material Efficiency In 2025
● Injection Molding Versus Other Processes
>> Injection Molding Vs Other Processes For OEMs
● Real World OEM Case Insights
● How To Choose An Injection Molding Partner In China
● Practical Steps To Start An Injection Molding Project
● Clear Call To Action For OEM Buyers
● FAQ: Injection Molding For OEMs
>> 1. What minimum order quantity is practical for injection molding
>> 2. How long does it take to build an injection mold
>> 3. Which materials are best for high strength plastic parts
>> 4. Can injection molding support overmolding and soft touch surfaces
>> 5. How does injection molding support sustainability goals
Injection molding offers fast, repeatable, and cost-effective production for OEMs that need high-quality plastic parts at scale. When combined with a reliable China-based OEM partner, it becomes a powerful way to shorten lead times, stabilize quality, and reduce total landed cost.

Injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten plastic is injected into a precision mold cavity, cooled, and then ejected as a solid part. The process is highly automated and designed for repeatable high-volume production.
Key characteristics for OEM buyers:
- High repeatability across thousands or millions of parts.
- Tight dimensional control suitable for demanding industries such as automotive, medical, and electronics.
- Compatibility with many engineering materials, from commodity plastics to advanced polymers.
This content targets OEM buyers, brand owners, and product companies searching for plastic injection molding solutions that can support long-term, stable production.
Primary keywords (to be woven naturally throughout the page):
- plastic injection molding advantages
- injection molding for OEMs
- custom injection molded parts
- injection molding manufacturer in China
- injection molding for high volume production
Long-tail, buyer-intent phrases:
- cost-effective injection molding for large production runs
- high-precision injection molding for complex parts
- how to choose an injection molding supplier in China
These phrases should appear in headings, introductory paragraphs, image alt text, and relevant internal links to product or service pages.
Injection molding is one of the most efficient methods for producing large volumes of identical plastic components. Once the mold is built and the process is tuned, cycle times can be measured in seconds rather than minutes.
Key efficiency benefits:
- Short cycle times enable rapid fulfillment of high-volume orders.
- Multi-cavity molds can produce several parts in a single shot to multiply output.
- Automation reduces manual handling and speeds up overall production flow.
Modern injection molding delivers very tight tolerances and excellent repeatability, especially when supported by robust design and process controls. The molten plastic fills even very small features inside the mold, enabling fine details and complex shapes.
Benefits for OEMs and brand owners:
- Consistent tolerances over long production runs, critical for assembly and functional performance.
- Freedom to integrate clips, threads, hinges, snap fits, logos, and other functional features directly into the part.
- Reduced need for secondary machining or manual finishing, which simplifies the overall process.
Once a mold is qualified, the injection molding process runs in a continuous loop that repeats the same cycle with high consistency. This repeated cycle is ideal for OEMs needing fast replenishment and predictable lead times.
Time-to-market advantages:
1. Fast cycle times per part enable quick ramp-up for new product launches.
2. Multi-cavity or family molds shorten schedules by producing multiple parts in one cycle.
3. Integrated post-processing options, such as molded-in color and texture, help avoid delays from downstream operations.
Injection molding supports a wide range of thermoplastics, thermosets, elastomers, and specialty materials, which allows engineers to tailor parts for specific performance needs. This versatility fits both consumer products and industrial applications.
Material-related benefits:
- Broad material selection including ABS, PC, PP, PA, PBT, TPU, and more, plus fillers and glass fiber reinforcement.
- Ability to tune mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties to match the application environment.
- Color, texture, and transparency can be controlled without secondary painting or coating.
Typical application sectors:
- Consumer electronics housings, connectors, and internal structural parts.
- Automotive interior components, clips, and under-the-hood parts.
- Medical device housings, consumables, and laboratory components.
Although injection molding requires upfront investment in tooling, the unit cost becomes very low once production volumes increase. This makes it a leading choice for OEMs that plan to produce thousands or millions of parts.
Key cost drivers:
- Economies of scale reduce unit cost as tooling expenses are spread over higher volumes.
- Automation minimizes labor per part compared with manual assembly or machining.
- Limited material waste and reduced post-processing help lower scrap and operational expenses.
Injection molding supports complex part design and functional integration that would be more difficult or expensive to achieve with many other manufacturing processes. This flexibility can streamline assemblies and improve product performance.
Design flexibility advantages:
- Integrated features such as ribs, bosses, living hinges, snap-fits, and guides can be molded in one shot.
- Multi-shot and overmolding allow the combination of rigid and flexible materials for enhanced functionality.
- Family molds can produce several related components together, which can simplify inventory and assembly.
Injection-molded parts generally come out of the mold with good surface quality, which can reduce or eliminate finishing operations. This is especially valuable for consumer-facing products that require a consistent cosmetic appearance.
Key finishing benefits:
- Molded-in texture and gloss that support the desired visual and tactile feel without painting.
- Less deburring, sanding, or polishing than many machined or cast parts require.
- Molded-in logos and markings that remove the need for separate labels or engraving.
Sustainability considerations increasingly influence material selection and manufacturing technology, and injection molding is no exception. Modern equipment and thoughtful process design can significantly reduce waste and energy usage.
Sustainability-related advantages:
- Closed-loop material systems and regrind use can reduce overall material consumption.
- Energy-efficient machines and optimized process parameters lower total power usage per part.
- Recyclable and bio-based polymers support environmentally conscious product lines and regulatory requirements.
OEMs often compare injection molding with CNC machining, 3D printing, and other processes during technology selection. Understanding strengths and trade-offs makes it easier to choose the right path for each project.
Aspect | Injection Molding | CNC Machining | 3D Printing (Additive) |
Best for volume | Medium to very high volumes (roughly 10,000+ parts) | Low to medium volumes with complex materials | Prototypes and small batches |
Unit cost at scale | Very low once tooling is amortized | Higher per part due to time and waste | Moderate to high, depending on print time |
Upfront investment | High mold and tooling cost | Low to medium setup cost | Low setup cost |
Design complexity | Excellent for complex, repeatable shapes | Good, though some shapes are inefficient or difficult | Excellent, especially for internal channels |
Surface finish | Mold defines smooth, cosmetic surfaces | Very good after machining, may require polishing | Visible layer lines are common |
Lead time to first parts | Tooling can take several weeks | Shorter if geometry is simple | Very short for first prototypes |
Material efficiency | Low scrap, with potential for regrind use | More waste from cutting operations | Low waste but slower throughput |
When OEMs move existing projects into a well-optimized injection molding setup, the results can be significant in both capacity and cost structure. Careful design and process planning are central to these improvements.
Typical outcomes include:
- Increased production capacity through the use of multi-cavity tools, automation, and optimized cycle times.
- Reduced overall part count by combining functions into single molded parts, which lowers assembly labor and inventory complexity.
These improvements can help OEMs maintain competitive pricing while still meeting demanding quality requirements.
For overseas brand owners and manufacturers, selecting a capable partner in China is a critical strategic decision. The right partner can support long-term product lifecycles with stable quality and predictable costs.
Key criteria to evaluate:
- Technical capability including in-house mold design, DFM support, and experience with tight-tolerance parts.
- Quality systems with clear standards, inspection procedures, and traceability.
- Material expertise to source and validate suitable engineering plastics and elastomers.
- Strong communication and project management, including clear timelines and responsive support.
It is especially helpful when the same partner also offers related services such as precision machining, silicone molding, and metal stamping for an integrated supply chain.
A structured project launch approach helps reduce risk and avoid costly changes later in the production journey. The following steps provide a practical roadmap.
1. Define requirements clearly
- Establish target annual volume, unit cost goals, lifetime expectations, and critical dimensions.
2. Optimize design for molding
- Collaborate on wall thickness, draft angles, gate locations, and parting lines to ensure robust manufacturability.
3. Select appropriate materials
- Balance mechanical performance, aesthetics, regulatory needs, and overall cost.
4. Approve tooling strategy
- Decide on single-cavity or multi-cavity tooling, family molds where appropriate, and allowances for future revisions.
5. Qualify with sampling
- Review initial samples, dimensional reports, and functional tests, and confirm any adjustments before mass production.
Following these steps makes it easier to reach stable mass production while avoiding extensive rework.
If you are a brand owner, wholesaler, or manufacturer looking to optimize plastic parts production, working with a partner that combines injection molding with precision machining, silicone manufacturing, and metal stamping can greatly simplify your supply chain. A single, integrated supplier can help shorten development cycles, stabilize quality across different components, and lower overall project risk.
Take the next step now: share your 3D files, drawings, and estimated volumes to receive a tailored recommendation on tooling, materials, and production strategy. Use the contact form or direct email on this site to request a detailed quotation and a professional design-for-manufacturing review. By providing project details today, you can quickly determine the best injection molding solution for your next product launch.
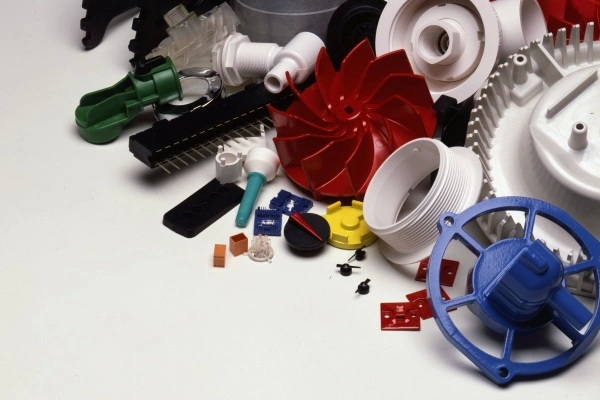

Injection molding is most cost-effective for medium to high volumes, typically starting from several thousand pieces per year. Lower volumes may still be feasible when parts are complex or require specific materials.
Typical lead times range from about three to eight weeks, depending on the complexity of the part, the size of the mold, and the material used for the tool. Sampling and validation add additional time before full production.
Engineering plastics such as polycarbonate, nylon, and certain glass-filled grades are commonly selected for high strength applications. The specific choice depends on required stiffness, impact resistance, and operating temperature.
Yes, overmolding and multi-shot molding can combine rigid substrates with soft elastomeric layers. This approach is widely used for grips, seals, protective edges, and other ergonomic or sealing functions.
Sustainability goals can be supported through the use of efficient machinery, process optimization, and recycled or bio-based plastics. Proper design and process control also help minimize scrap and extend tool life.