Milling Machining: Different Types of Milling Operations for Precision Parts
What is Milling in Machining?
Milling is a machining process that involves the removal of material using rotary cutters to create a desired shape or form. It is commonly used in the manufacturing industry to produce CNC precision machining parts with complex geometries.
What Is the Importance of Milling Machining?
– Versatility:
Milling machines can perform a wide range of machining operations. They can create complex shapes and contours on a variety of materials. They are suitable for diverse applications across industries.
–Precision:
Milling offers a high level of precision and accuracy in producing parts. The ability to control the dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes with precision. It ensures that the final products meet the required specifications and quality standards.
– Efficiency:
Milling machines are capable of removing material at high speeds, allowing for efficient material removal rates. This results in shorter production cycles, reducing lead times, and increasing productivity.
– Flexibility:
With different types of milling operations and a variety of cutting tools available, milling provides flexibility in manufacturing. It enables to produce a wide range of parts with varying complexities.
– Cost-Effectiveness:
Milling is a cost-effective machining method, especially for producing complex parts. By using a single milling machine, multiple operations can be performed without tool changes. This reduces setup times, labor costs, and overall production expenses.
– Integration with CAD/CAM Systems:
Milling machines can be seamlessly integrated with computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems. This integration enables precise control and automation of the milling process.
What are the Common Milling MachiningMaterials?
– Metals:
Metals such as steel, aluminum, and copper are commonly milled for applications in automotive, aerospace, and general engineering industries.
– Plastics:
Plastics like ABS, PVC, and nylon are milled for manufacturing components in industries such as consumer electronics and medical devices.
– Composites:
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRP), are milled to create lightweight and strong parts used in aerospace and sports equipment.
– Woods:
Milling is used to shape and carve wooden components for furniture, cabinetry, and other woodworking applications.
– Ceramics:
Ceramics, including porcelain and advanced ceramics, can be milled to create intricate shapes. They are used in the production of electronic components and dental prosthetics.
–Others:
Milling can also be applied to materials like foam, rubber, and certain types of glass, depending on their properties and machinability.
What is Milling Machine Operation?
Milling machine operations refer to the various tasks and operations performed using a milling machine. The milling cutter has multiple cutting edges that can remove material in the form of chips.
The Types of Milling operations can be divided into basic milling machining and advanced milling machining, details are as followed:
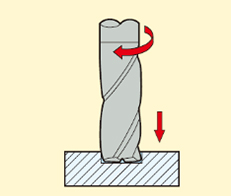
1.Face Milling
The end teeth of the cutter engage with the workpiece surface. It is commonly used for creating a flat surface such as plates, bases, and mechanical parts.
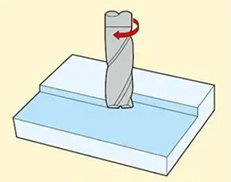
2.Slot Milling
Machining through the cutting diameter fully engaged with the workpiece surface. It is commonly used for creating slots or grooves.
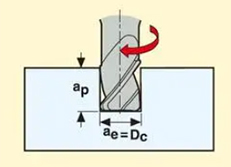
3.Side Milling
Machining by engaging the side of the the cutter with the workpiece surface. It is used to create flat or contoured surfaces, or others.
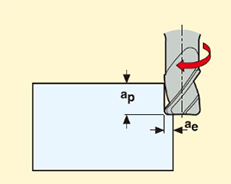
4.Profile Milling
Machining by utilizing the engagement of the ball nose end mill with the workpiece surface. It is used to create complex curved surface shapes and specific contours.
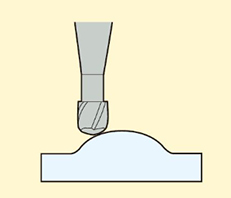
5.Ramp Milling
Milling a workpiece with a cavity at a certain angle in the Z-axis direction. It is commonly used to process workpiece with inclined surfaces, such as inclined platforms, ramps, or sloped grooves.
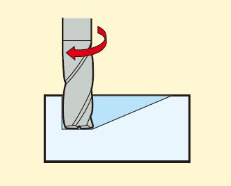
6.Helical Interpolation Ramp Milling
The cutter performs Z-axis ramp milling while also undergoing circular motion to mill a cavity. It is commonly used for machining workpieces with helical or ramp cavity shapes.
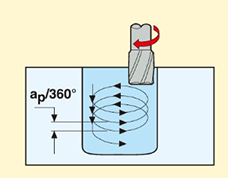
7.Trochoidal Milling
Partial circular motion is performed along the X or Y axis, and slotting is carried out using a side milling cutter. It is used for machining slotted workpieces with specific profiles.
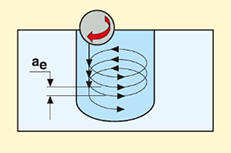
8.Push-Pull Copy Milling
Machining a 3D contour by performing up and down contouring movements along the profile of the surface. It is a favored choice in modern machining practices to enhance precision and efficiency.
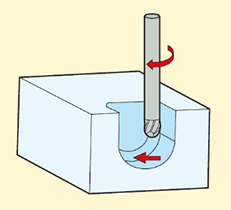
9.Plunge Milling
Creating a deep groove by drilling in the Z-axis. The milling cutter is positioned vertically to the workpiece surface and performs downward cutting along the axial direction. It is suitable for machining deep grooves, pockets or cavities.
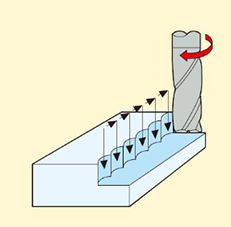
10.Contour Milling
A small amount of drilling or ramp milling is performed in the Z-axis, followed by milling the cavity along the X and Y axes. It is suitable for machining complex cavities, molds, and surface finishing of parts.
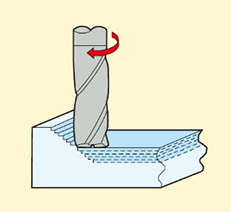
11.Drilling
Creating a hole by moving along the Z-axis. A rotating cutter is lowered into the material along the vertical direction of the workpiece surface to form a smaller diameter hole. It is suitable for creating accurate circular holes.